The roof of ventricle is diamond shaped and can be divided into superior and inferior parts.
Roof of 4th ventricle.
It corresponds to the ventral surface of the cerebellum.
The obex is the most caudal tip of the fourth ventricle.
Fourth ventricle sagittal section of the brain.
The roof of fourth ventricle is the dorsal surface of the fourth ventricle.
The fourth ventricle has a roof at its upper posterior surface and a floor at its lower anterior surface and side walls formed by the cerebellar peduncles nerve bundles joining the structure on the posterior side of the ventricle to the structures on the anterior side.
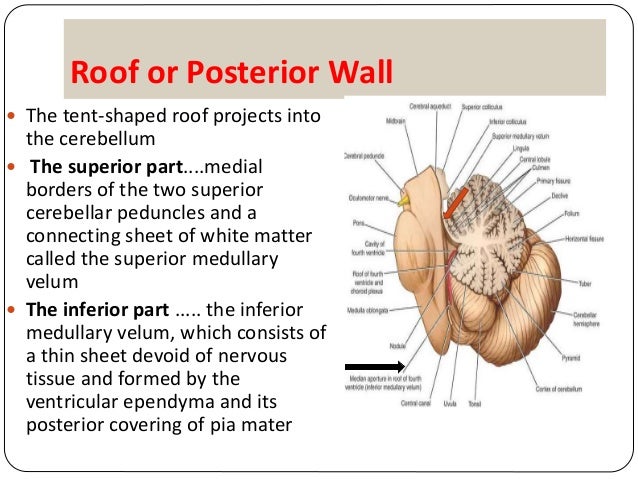
The superior part of the roof is formed by the superior cerebellar peduncles and the superior medullary velum thin sheet of white matter.
In the upper part it is formed by superior medullary velum white matter between the superior cerebellar peduncles.
The roof of fourth ventricle is tent shaped and is divided into upper and lower part.
The roof of fourth ventricle is the dorsal surface of the fourth ventricle.
The upper part of the roof is composed by a thin sheet of white matter the superior medullary velum that stretches between both superior cerebellar peduncles.
Superior medullary velum c.
It corresponds to the ventral surface of the cerebellum.
The roof of the fourth ventricle is tent shaped rising to an apex called the fastigium that divides the superior roof from the inferior roof.
The roof of the fourth ventricle has presents a tent like apex at the intersection of it s superior and inferior parts.
Flat floor of fourth ventricle sign.
The upper portion of the roof is formed by the cerebellum.
Roof the fourth ventricle is formed by all of the following except.
Inferior medullary velum b.
The apex of the tent goes posteriorly into the white core of the cerebellum.
Median eminence is seen in the floor of the fourth ventricle.
The median part of the superior roof called the superior medullary velum consists of a thin lamina of white matter between the cerebellar peduncles.
This apex also known as the fastigium extends into the white core of the cerebellum.